What is pulse oximetry?
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring a person's oxygen saturation. It is used to measure the oxygen level in your blood and your heart rate.
How does pulse oximetry work?
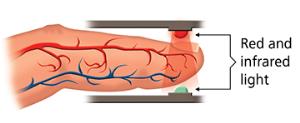
A finger pulse oximeter functions by shining light through your finger. The sensors detect how much oxygen is in your blood based on the way the light passes through your finger. Pulse oximetry is the technology calculating the results to display a number on the oximeter’s screen that tells you the percent of oxygen in your blood. A finger pulse oximeter also measures your pulse rate.
Checking For Sleep Apnea
This video shows you how you can check if you have sleep apnea, using a rough estimate based on oxygen desaturation events, using pulse oximetry. It is important to note that this will not tell you if you definitely have sleep apnea and is no substitute for a doctor. Please see a doctor if you feel you have sleep apnea.
This video uses the CMS50E pulse oximetry.
Oxygen Desaturation Index (ODI)
When you record your pulse oximetry, you can obtain your ODI (Oxygen Desaturation Index). ODI is the number of times per hour of sleep that your blood's oxygen level dropped from the baseline. It may not be as accurate as other ways of monitoring sleep unless the stages of sleep are also recorded.
Any respiratory event during sleep with a 3-4 percent drop in blood oxygen level, lasting 10 seconds or more, is an ODI event. An example of an oxygen desaturation event would be a change from 95 to 92 percent.
Limitations of oximetry
Pulse oximetry has many well known limitations. The amount of ambient light, skin pigmentations, nail polish usage, the temperature of the hand, interference and other factors can impact its reading. A pulse oximeter also does not know if you are asleep so the readings cannot be considered as accurate as AHI, which needs to be obtained using other technology.
Limitating factors (source):
-
Carbon monoxide
-
Cabon monoxide molecules, even in small amount, can attach to the patient's hemoglobin replacing oxygen molecules. A pulse oximeter cannot distinguish differences and will show total saturation level of oxygen and cabon monoxide.
-
-
Hemoglovin deficiency (anemia)
-
Blood volume deficiency
-
Irregular signals such as irregular heartbeats
-
External interference
-
Exposure to strong external light while taking a reading can give inaccurate readings
-
-
Fingernail polish and pressed nails
-
Nail polish and pressed-on nails may interfere with readings and should be removed
-
-
Skin pigmentation
-
Dark skin can give over-estimated SpO2 readings when it is below 80%
-
-
Intraveneous dyes
-
Intraveneous dyes (such as methylene blue, indigo carmine and indocyanine green) can cause inaccurate readings
-
-
Methemoglobin
-
Methemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that does not carry oxygen. The higher the percentrage of methemoglobin can be genetic or caused by exposure to certain chemicals and medications.
-
Pulse Oximetry and Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is often measured in terms of AHI (apnea hypopnea index) per hour. This is the amount of times someone stops breathing while they sleep per hour.
A pulse oximeter cannot give AHI but it can give ODI (oxygen desaturation index). ODI is an approximation of AHI and is considered a good predictor (source).
Sleep apnea AHI levels:
-
Normal - less than 5 AHI/ hour
-
Mild sleep apnea - 5 to 15 AHI/ hour
-
Moderate sleep apnea - 15 - 30 AHI/ hour
-
Severe sleep apnea - 30 or more AHI/ hour
By recording your oxygen desaturation events at night per hour and relating them to AHI, you can have an estimate for the presence of sleep apnea. We've reviewed the best overnight pulse oximeters here.
A pulse oximeter is not as accurate in diagnosing sleep apnea as a polysomnograph.
What is abnormal in pulse oximetry measurement?
In general, it's considered abnormal if the oxygen level falls below 88% for an adult or below 90% in a child. If the levels are below 88% for longer than 5 minutes a night, a condition known as hypoxemia may be diagnosed.
Pros and Cons of Overnight Oximetry
Pros:
-
Easy and inexpensive
-
Devices can be purchased in many places
-
Can be useful to see if someone needs further testing with a polysomnograph
Cons:
-
Oximetry alone is not adequate to diagnose sleep apnea
-
Cannot be used for insurance purposes
-
Is not as accurate as AHI
-
Cannot detect central sleep apnea
Oximetry Is No Substitute For A Doctor
You should see a doctor if you believe you may have sleep apnea. Oximetry is merely a low cost, at home way to monitor an approximatation of sleep apnea.
FAQ: Pulse Oximetry
How does pulse oximeter work?
A pulse oximeter is a small, clip-like device that measures the oxygen saturation in the blood. It's a non-invasive tool that provides instant feedback on the oxygenation of a patient's blood. Here's how it works:
-
Principle of Spectrophotometry: The pulse oximeter works on the principle of spectrophotometry. Blood with oxygen is bright red, while blood without enough oxygen is darker. By analyzing the colors of the light absorbed and reflected by the blood, the device can determine the oxygen saturation.
-
Light Emission: The oximeter has small light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that shine light through a relatively translucent area of the patient's body, typically a fingertip or earlobe.
-
Two Wavelengths: The device emits light at two wavelengths: red light (around 660 nanometers) and infrared light (around 940 nanometers). Oxyhemoglobin (oxygen-bound hemoglobin) and deoxyhemoglobin (oxygen-free hemoglobin) absorb different amounts of each light. Oxyhemoglobin absorbs more infrared light and lets more red light pass through, while deoxyhemoglobin does the opposite.
-
Light Detection: On the opposite side of the light source, in the oximeter, there's a photodetector or light sensor. This sensor measures the amount of light that passes through or is reflected back from the finger.
-
Pulse Detection: The oximeter also detects the pulse rate. It does this by noting the change in light absorption during the surge of a fresh pulse of blood with every heartbeat.
-
Calculation: Using the information from the light absorption, the oximeter then uses a complex algorithm to calculate the percentage of hemoglobin molecules carrying oxygen in the blood. This percentage is known as the oxygen saturation, or SpO2, and it's displayed on the oximeter's screen. A healthy individual typically has an SpO2 value between 95% and 100%.
-
Display: Most pulse oximeters display both the oxygen saturation and the heart rate.
In essence, a pulse oximeter is a valuable tool because it allows for continuous, non-invasive monitoring of a patient's oxygenation, giving healthcare providers immediate feedback on a patient's respiratory status.
How accurate is a pulse oximeter?
Pulse oximeters are generally quite accurate. A standard pulse oximeter typically has an accuracy of ±2%. This means if your reading is 95%, your true oxygen saturation might be anywhere from 93% to 97%. However, the accuracy can be influenced by factors like poor circulation, skin pigmentation, nail polish, and artificial nails.
What are three conditions that can give a false pulse oximetry reading?
-
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Hemoglobin that's bound to carbon monoxide (carboxyhemoglobin) can be wrongly identified as oxyhemoglobin by some pulse oximeters, which can lead to falsely elevated readings.
-
Methemoglobinemia: Methemoglobin is an altered state of hemoglobin that can't bind to oxygen. Elevated levels of methemoglobin can cause some oximeters to read falsely high or low.
-
Peripheral Vasoconstriction: Conditions that lead to reduced peripheral blood flow, such as hypothermia, Raynaud's phenomenon, or certain medications, can interfere with the oximeter's ability to detect a pulse, potentially leading to inaccurate readings.
How can an oximeter detect oxygen?
An oximeter detects oxygen by shining light through a translucent part of the body (like a fingertip) and measuring how much light is absorbed by the oxygen-rich hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin) and oxygen-poor hemoglobin (deoxyhemoglobin). Since these two types of hemoglobin absorb light at different wavelengths, the oximeter can determine the ratio between them and calculate the percentage of hemoglobin molecules carrying oxygen (oxygen saturation or SpO2).
Why am I short of breath but my oxygen saturation is good?
Even if your oxygen saturation reads as normal, you can still experience shortness of breath. This can be due to various reasons unrelated to oxygen levels, such as:
- Lung conditions like chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or pulmonary fibrosis.
- Anxiety or panic attacks.
- Heart conditions like heart failure or arrhythmias.
- Muscle or skeletal issues restricting the movement of the chest or diaphragm.
If you're experiencing unexplained shortness of breath, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.


